
Cytoskeletal elements interact extensively and intimately with cellular membranes. What are two functions of the cytoskeleton.
All cells have a cytoskeleton but usually the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells is what is meant when discussing the cytoskeleton.
What are two functions of the cytoskeleton. Beside this what are two capabilities of the cytoskeleton quizlet. The cytoskeleton helps and shapes a cell helps place and transport organelles gives energy assists in cell division. The cytoskeleton is a network of microfilaments intermediate filaments and microtubules.
The cytoskeleton has a variety functions including giving shape to cells lacking a cell wall allowing for cell movement enabling movement of organelles within the cell endocytosis and cell division. Cytoskeleton Functions The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below. It provides shape and support to the cell.
It helps in the formation of vacuoles. It holds different cell organelles in place. It assists in cell signalling.
1 Function of the Cytoskeleton – Provides structure support to the cell 2 Function of the Cytoskeleton – Stabilizes junctions between cells This 14 words question was answered by John B. On StudySoup on 5312017. The question contains content related to Physics and Science.
Since its upload it has received 113 views. A cells cytoskeleton ensures stability energy and motility. This provides a cellular scaffolding that arranges the cellular organization into.
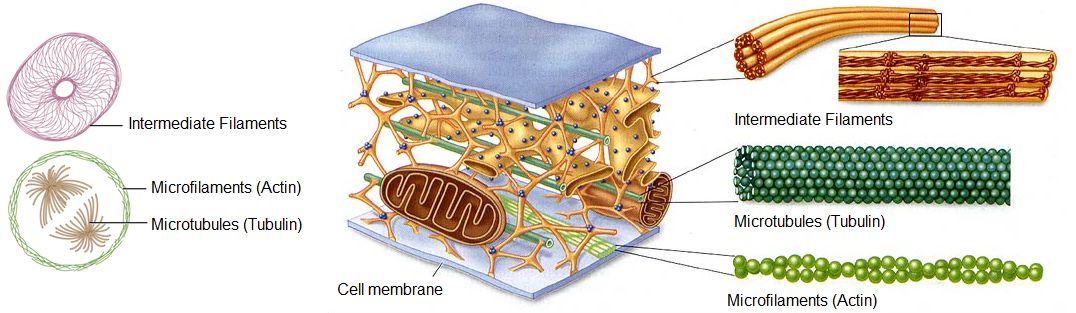
The figure represents a part of the cytoskeleton of a cell. Note the cytoskeleton is extremely extensive. Notice that the cytoskeleton seems to.
The cytoskeleton supports the cell gives it shape organizes and tethers the organelles and has roles in molecule transport cell division and cell signaling. Structure of the Cytoskeleton. All cells have a cytoskeleton but usually the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells is what is meant when discussing the cytoskeleton.
What are two functions of the cytoskeleton. Was asked on May 31 2017. View the answer now.
What are the functions of the cytoskeleton. Click card to see definition. Tap card to see definition.
The cytoskeleton supports and shapes the. Cell positions and transports organelles provides strength assists in cell division and aids cell movement. Click again to see term.
The cytoskeleton assists in the transportation of communication signals between cells. It forms cellular appendage-like protrusions such as cilia and flagella. What are two functions of the cytoskeleton.
The cytoskeleton is a network of microfilaments intermediate filaments and microtubules. The cytoskeleton performs a number of functions including the formation of cells that do not have a cell wall so that cell movements allow for the movement of organelles within the cell endocytosis and cell division. 1- Cytoskeleton support the transportation of vesicles into and out of a cell.
2-It makes cell migration possible like cell motility which is needed to build up tissues. 3- Microfilaments are involved in endocytosis and exocytosis. 4-The cytoskeleton help in the.
The cytoskeleton provides the cell with structure and shape and by excluding macromolecules from some of the cytosol it adds to the level of macromolecular crowding in this compartment. Cytoskeletal elements interact extensively and intimately with cellular membranes. Cytoskeletons primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation.
The cytoskeleton can also contract thereby deforming the cell and the cells environment which allows the cells to migrate. Cytoskeleton is involved in many cell signalling pathways and in the. Because of its localization in different types of cells the cytoskeleton system is known for its role in providing internal scaffold that helps maintain the structural integrity of a cell.
Apart from maintaining the shape of a cell however it serves several other functions in cells. Cytoskeleton a system of filaments or fibers that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell maintains the cells shape and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself and the movement of the various organelles within it.
The Function Of a Cytoskeleton. As the name implies a cytoskeleton is the frame that gives shape to a cell. Just like in a human being the skeleton also helps hold all of the organelles organs in people in place.
Finally it also assists in moving materials in and out. The cytoskeleton is a dynamic scaffold inside all eukaryotic cells that is responsible for cell shape and motility as well as the transport and organization of intracellular components. The cytoskeleton is composed of three classes of protein polymers called microtubules microfilaments and intermediate filaments each formed by the self-association of protein subunits.
The cytoskeleton is responsible for contraction cell motility movement of organelles and vesicles through the cytoplasm cytokinesis establishment of the intracellular organization of the cytoplasm establishment of cell polarity and many other functions that. 6 It keeps a relation with sensory functions and transport processes across membranes insofar that most recep-tors and channels are attached to the cytoskeleton 5 79. The receptor function is most pronounced in sensory cilia.
Since the cytoskeleton is part of the broader structure of the cell-matrix all these functions also belong to the latter.