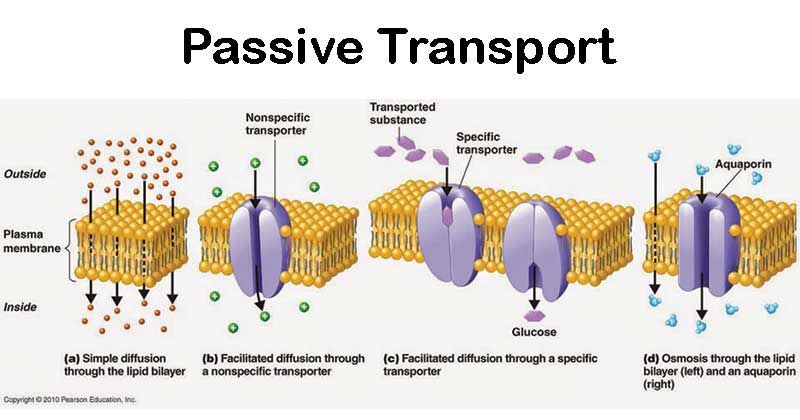
The passive forms of transport diffusion and osmosis move material of small molecular weight. Moving against a gradient To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient a cell must use energy.
Instead of using cellular energy like active transport passive transport relies on the second law of thermodynamics to drive the movement of substances across cell membranes.
Three forms of passive transport. There are three main kinds of passive transport - Diffusion Osmosis and Facilitated Diffusion. What types of transport are passive. The rate of passive transport depends on the permeability of the cell membrane which in turn depends on the organization and characteristics of the membrane lipids and proteins.
Facilitated diffusion is the passive transportation of ions or molecules across the cell membrane through specific transmembrane integral proteins. The molecules which are large and insoluble require a carrier substance for their transportation through the plasma membrane. This process does not require any cellular or external energy.
Three common types of passive transport include simple diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion. What are 2 types of active transport. There are two main types of active transport.
The passive forms of transport diffusion and osmosis move material of small molecular weight. Substances diffuse from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration and this process continues until the substance is evenly distributed in a system. There are four different types of passive transport.
Diffusion facilitated diffusion filtration and osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area with lower concentration. Passive Transport Definition.
Passive transport also known as passive diffusion is a process by which an ion or molecule passes through a cell wall via a concentration gradient or from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Its like moving from the train to the platform of a subway station or stepping out of a crowded room. Simple diffusion assisted diffusion filtration and osmosis are the four primary forms of passive transport.
Three common types of passive transport include simple diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion. Simple Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area. There are three forms of passive transport or the movement of biochemical and other atomic or molecular substances across the cell membranes.
Three common types of passive transport include simple diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion. Why would a cell use active transport. Moving against a gradient To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient a cell must use energy.
Types of Transport Across Cell Membranes 1 Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane 2 Passive Transport 3 Passive Transport Simple Diffusion Doesnt require energy Moves high to low concentration Example. Oxygen or water diffusing into a cell and carbon dioxide diffusing out. 4 Simple Diffusion Requires NO energy Molecules move from area of HIGH to LOW.
The transport across cell membrane is classified into three types. Types of transport across cell membrane are listed below. Active transport requires energy in the form of ATP solute from lower concentration to higher concentration transport through cell membrane.
Passive transport is a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes. Instead of using cellular energy like active transport passive transport relies on the second law of thermodynamics to drive the movement of substances across cell membranes. Fundamentally substances follow Ficks first law and move from an area of high concentration to.
Three forms of cellular movement are shown below. Passive transport of solutes across cell membranes from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. This movement continues until equilibrium is reached on both sides of the membrane.
Membrane Transport and its Types Passive and Active Transport and its Transporters Introduction. Membrane lipid bilayers have a hydrophobic interior which prevents the passage of most polar molecules. The barrier function of lipid bilayer permits maintenance of concentrations of solute in its cytosol which differ from the extracellular environment.