
The supply of the female urethra takes place through the Corpus spongiosum urethrae which designate the plexus. It starts at the Ostium urethrae internum and ends at the Glans penis the Ostium urethrae externum.
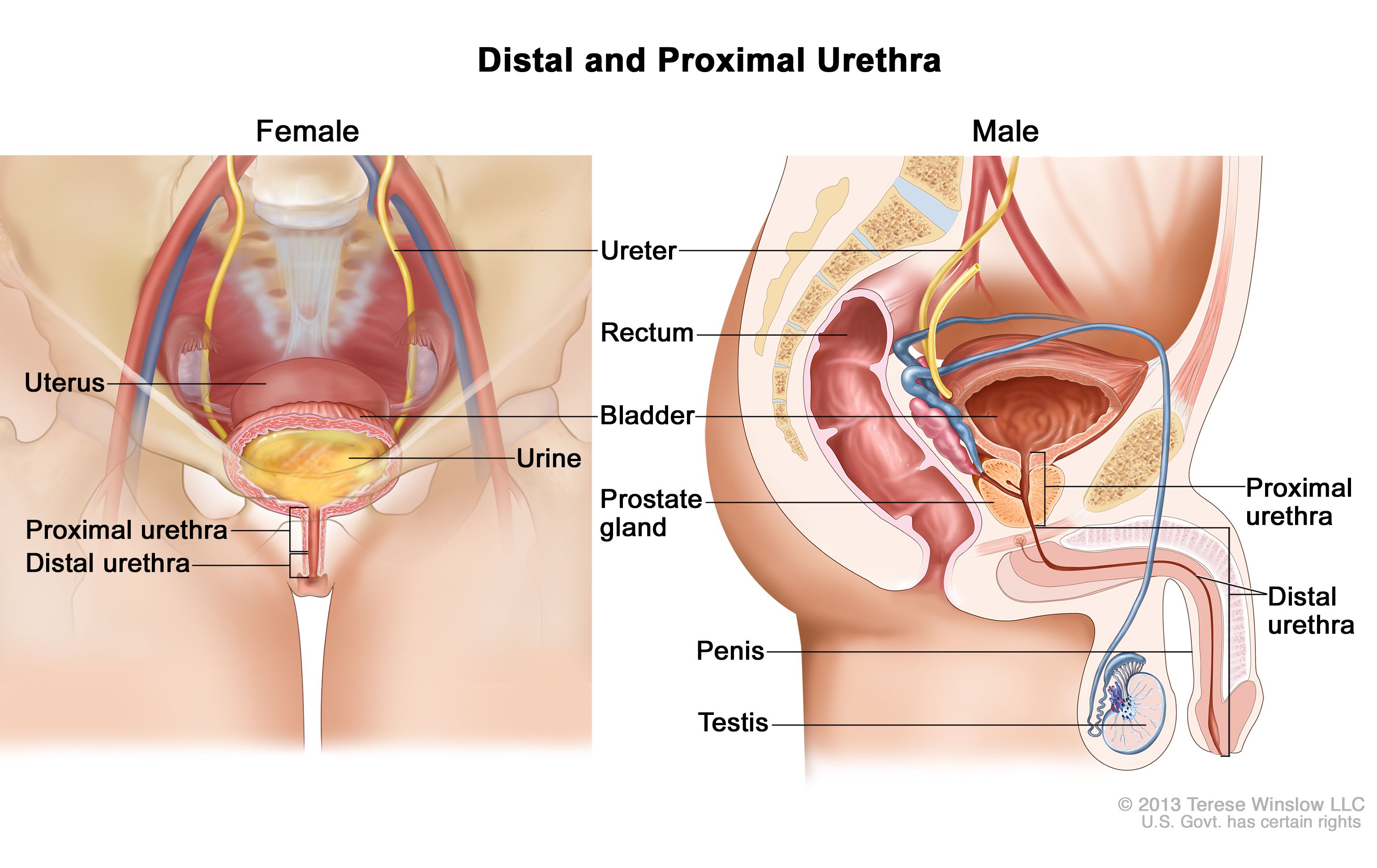
The male urethra connects the urinary bladder to the penis.
Structure and function of the urethra. Urethra Function and Structure In females the main urethra functions are the transportation of urine out of the body prevention of urine reflux and protection against pathogenic bacteria. Resembling a tubular structure it develops a connection between the urinary bladder and the genital organs in your body. The urethra pictures will make the thing clear to you.
It is this canal carrying the excretory fluids that opens to the exterior of the body. The length of urethra varies greatly across genders that is females and males. Urethra duct that transmits urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body during urination.
The urethra is held closed by the urethral sphincter a muscular structure that helps keep urine in the bladder until voiding can occur. Learn more about the urethra in this article. Structure of the Urethra.
The urethra is surrounded by two sphincters that open and close to allow for the passage of urine. The external sphincter and the internal sphincter. The urethra is the tube that releases urine from the body through the exit from the urinary tract known as the urinary meatus.
The urethra is 1 ½ inches in females and in males the urethra is 6. The urethra is the vessel that transports urine from the bladder to an external opening in the perineum. The anatomical course of the urethra is different in men and women.
The urethra is the excretory canal of the urinary bladder. It conveys urine from the urinary bladder to outside the body. It extends from the internal urethral orifice of the bladder to the external urethral orifice of the external genitalia.
The course of urethra is different between males and females. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of your body. In males it has the additional function of expelling ejaculating semen when you reach orgasm.
When the penis is erect during sex the flow of urine is blocked from the urethra allowing only semen to. The male urethra connects the urinary bladder to the penis. Once the bladder becomes full urine flows through the urethra and leaves the body at the urethral meatus which is located at tip of.
The elementary structure of the ureter is elastic muscles entangled in fiber layers that allow to control the sphincter. The muscular layers cover the whole path between the kidney to the bladder. The kidneys produce urine by filtering excess water from our blood.
The blood transports the debris to the kidneys. In males the urethra size- 20 cm allows for the expulsion of both urine and semen. Internal and external urethral sphincter muscles control micturition.
In females the main urethra size 3-4 cm functions are the transportation of urine out of the body prevention of. This is a muscular structure in the urethra that helps hold urine inside the body until its released. The urethra opens into the vestibule the area between the labia minora.
The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the external urethral orifice and out of the body. Structure of the Urinary Bladder Urine produced by the kidneys moves through the ureters and enters the bladder. The supply of the female urethra takes place through the Corpus spongiosum urethrae which designate the plexus.
The male urethra has an average length of 2025 cm. It starts at the Ostium urethrae internum and ends at the Glans penis the Ostium urethrae externum. Its task is besides the passing of urine the transport of seminal fluid.
Like the female urethra the male urethra gets rid of urine. It also releases semen during ejaculation. Function of Urinary System The urinary system or renal system is made up of the organs tubes muscles and nerves that work together to create store and excrete urine.
In general the urethra consists of a mucosal tube surrounded by a vascular submucosa and muscular tunic. Between 20 and 44 of urethral wall volume is connective tissue and the urethral wall volume increases distally. 34 The urethral mucosa is composed of transitional epithelium that forms longitudinal folds when relaxed.
The lining becomes stratified squamous epithelium near the external. The kidneys form the urine and account for the other functions attributed to the urinary system. The ureters carry the urine away from kidneys to the urinary bladder which is a temporary reservoir for the urineThe urethra is a tubular structure that carries the urine from the urinary bladder to the outside.
Although a main function of the penile urethra is to transport urine and semen the urethra is surrounded by vascular sponge like tissue called corpus spongiosum and this spongy vascular tissue also expands during an erection. Copulatory organ designed to deliver sperm into the female reproductive tract. Internally the this contains the spongy urethra and three long bodies of erectile tissue which are a spongy network of tissue riddled with spaces.
During sexual excitement blood fills these.