Noun An example of a cell wall is the rigid. Many prokaryotic cells also have cilia tails or other ways in which the cell can control its movement.

What does cell-wall mean.
Simple definition of cell wall. The cell wall is the outer covering of a cell present adjacent to the cell membrane which is also called the plasma membrane. As mentioned earlier the cell wall is present in all plant cells fungi bacteria algae and some archaea. Definition of cell wall.
The usually rigid nonliving permeable wall that surrounds the plasma membrane and encloses and supports the cells of most plants bacteria fungi and algae. A cell wall is the wall of a cell in plants bacteria fungi algae and some archaea. Animal cells do not have cell walls nor do protozoa.
Cell walls protect the cells from damage. It is also there to make the cell strong to keep its shape and to control the growing of the cell and plant. The outermost layer of cells in plants bacteria fungi and many algae that gives shape to the cell and protects it from infection.
In plants the cell wall is made up mostly of cellulose determines tissue texture and often is crucial to cell function. The American Heritage Science Dictionary Copyright 2011. Cell wall - a rigid layer of polysaccharides enclosing the membrane of plant and prokaryotic cells.
Maintains the shape of the cell and serves as a protective barrier. The cell wall is the protective semi-permeable outer layer of a plant cell. A major function of the cell wall is to give the cell strength and structure and to filter molecules that pass in and out of the cell.
Updated August 26 2019. A cell wall is a rigid semi-permeable protective layer in some cell types. This outer covering is positioned next to the cell membrane plasma membrane in most plant cells fungi bacteria algae and some archaea.
Animal cells however do not have a cell wall. Definition for cell wall. The cell wall is the outermost boundary in the majority of prokaryotes and plant cell eukaryote.
It is a structural layer that surrounds some type of cells present just outside the cell membrane. The prokaryotic cell wall is a semi-rigid non-living component of the cell that surrounds the plasma membrane. A cell wall is a strong protective structure that surrounds a plant cell.
It has holes called plasmodesmata that allow substances to move in and out of the cell. Essentially the cell wall is a complex highly organized structure that defines the shape of a plant cell its also found in bacteria fungi algae and archaea. In addition to defining the shape of plant cells a cell wall has a few other functions that include maintaining the structural integrity of a cell acting as a line of defense against.
Cell wall also takes part in the processes of carbon flow through ecosys-tems. The organic substances that make up humus in the soil and that enhance soil structure and fertility are derived from cell walls. Finally as an important source of roughage in our diet the plant cell wall is a significant factor in human health and nutrition.
Osmosis Simple Definition Biology - Cell Wall - Biology Encyclopedia - cells plant body. Cell membrane from an area of. Osmosis is a biophysical process occurring commonly in biological systems where solvent molecules move across a.
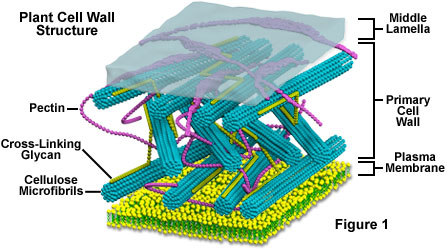
The cell wall is the most prominent part of the plants cell structure. It is made up of cellulose hemicellulose and pectin. The cell wall is present exclusively in plant cells.
It protects the plasma membrane and other cellular components. The cell wall is also the outermost layer of plant cells. What does cell-wall mean.
The definition of a cell wall is the protective coating for a plant cell. Noun An example of a cell wall is the rigid. Many prokaryotes have a cell membrane made of phospholipids enclosed by a cell wall made of a rigid sugar.
The cell wall may be enclosed by another thick capsule made of sugars. Many prokaryotic cells also have cilia tails or other ways in which the cell can control its movement. These characteristics as well as the cell wall and capsule reflect the fact that prokaryotic cells.
Plant Cell Wall. It is a rigid layer that is composed of cellulose glycoproteins lignin pectin and hemicellulose. It is located outside the cell membrane and is completely permeable.
The primary function of a plant cell wall is to protect the cell against mechanical stress and to provide a definite form and structure to the cell. The functions of cell wall are. It provides protection to the cell and prevents from any physical damage.
It provides structure to the cell. It prevents from osmotic bursting. It protects the protoplasm against mechanical injury.
It controls intercellular transport. As the name suggests the cell wall is the outer covering of the plant cell. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect the inner components of the plant cell.
But this is not its only function. This component is also giving the plant cell its shape. In the plant cell the constituents of the cell wall are mainly.