
H K NH3 urea creatinine histamine and drugs like penicillin. Secretion which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine.
At the same time waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubule.
Secretion in the nephron. What is secreted in nephron. Secretion which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine. Secreted substances include potassium ions hydrogen ions and some xenobiotics.
What are the two main parts of the nephron. A nephron is made of two parts. At the same time waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubule.
This process is called secretion. The secreted ions combine with the remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into a collecting duct.
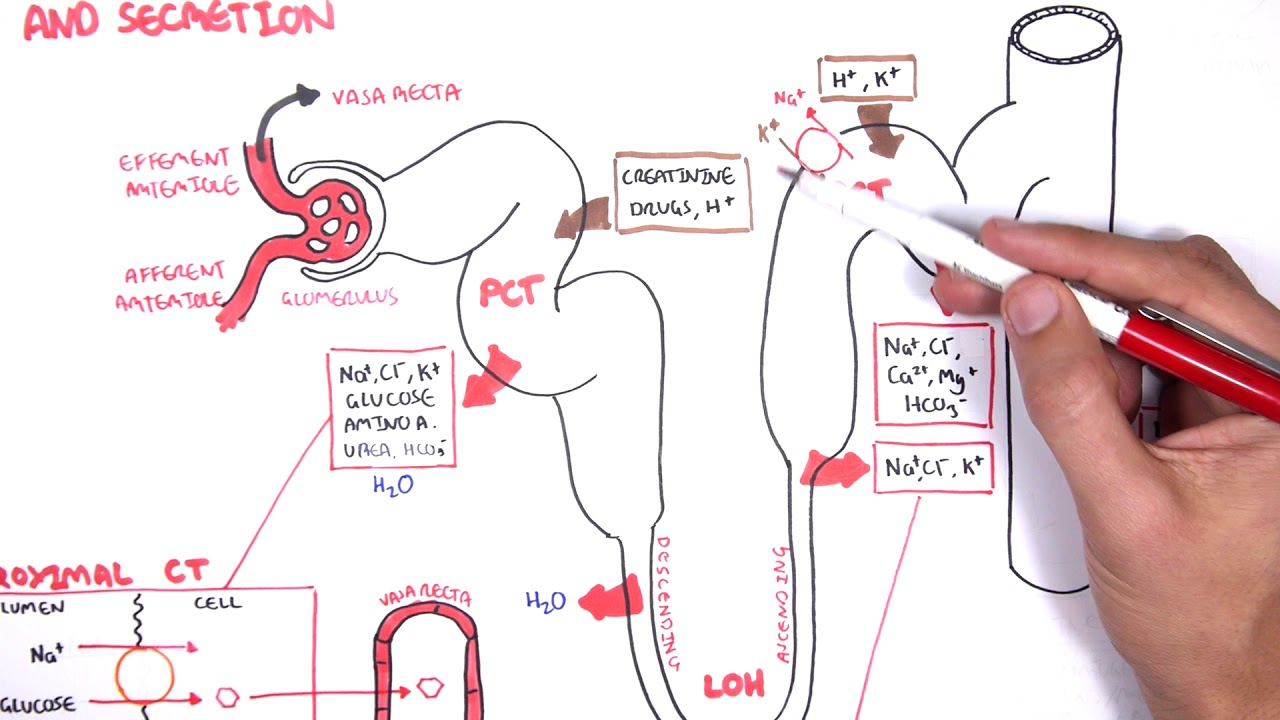
The secretion of H in this section of the nephron is mainly a result of the Na H antiporter in the apical membrane using secondary active transport. HCO 3-is reabsorbed here in a different way to other substances. The presence of hydrogen in the lumen causes some amount of it to dissociate to carbon dioxide and water via the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
In humans and other vertebrates tubular secretion occurs in the kidneys where the blood is filtered in specialized structures known as nephrons. These structures consist of a long tubule surrounded by extensive capillaries. Tubular secretion occurs throughout the different parts of the nephron from the proximal convoluted tubule to the collecting duct at the end of the nephron.
Hydrogen Ion Secretion The tubular secretion of H and NH 4 from the blood into the tubular fluid is involved in blood pH regulation. The primary function of nephron is removing all waste products including the solid wastes and other excess water from the blood converting blood into the urine reabsorption secretion and excretion of numerous substances. Secretion which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine.
Secreted substances include potassium ions hydrogen ions and some xenobiotics. Start studying Secretion and Re-absorption in the nephron. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Physiology of the Nephron. An example of a primary active transport mechanism. - Mechanism for glucose molecules to move down their concentra.
- Mechanism for glucose molecules to move into a. This is the process of moving waste products that have remained in the bloodstream into the renal tubule so that they can be excreted with the urine. Essentially the job of the nephron.
What is reabsorbed and secreted in the nephron. Each nephron begins with a filtration component that filters the blood entering the kidney. The major functions of these lining cells are the reabsorption of water and small molecules from the filtrate into the blood and the secretion of wastes from the blood into the urine.
Secretion moves solutes from the blood and nephron tubule cells into the tubular fluid. Secretion is important for removal of substances that arent filtered such as drugs and metabolites and for fine-tuning the final urine composition. Secretion which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine.
Secreted substances include potassium ions hydrogen ions and some xenobiotics. List the locations in the nephron where tubular secretion occurs Describe how where and what substances are secreted by the nephron. With up to 180 liters per day passing through the nephrons of the kidney it is quite obvious that most of that fluid and its contents must be reabsorbed.
Nephron functional unit of the kidney. This tutorial explores the function of the nephron in particular. Filtration Reabsorption Secretion and Excretion.
The nephron uses four mechanisms to convert blood into urine. Filtration reabsorption secretion and excretion. 395396 These apply to numerous substances.
The structure and function of the epithelial cells lining the lumen change during the course of the nephron and have segments named by their location and which reflects their. The principle task of the nephron population is to balance the plasma to homeostatic set points and excrete potential toxins in the urine. They do this by accomplishing three principle functionsfiltration reabsorption and secretion.
Tubular secretion occurs throughout the different parts of the nephron from the proximal convoluted tubule to the collecting duct at the end of the nephron. What is secreted by the renal tubules. Substances mainly secreted into renal tubule are.
H K NH3 urea creatinine histamine and drugs like penicillin. Simply so where does secretion occur in the nephron. Secretion which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine.
Furthermore what are the parts of a nephron. Secretion which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine. Know more about it here.
Likewise people ask what are nephrons how do they help in the excretion of waste. What is secreted in nephron. Secreted substances largely include hydrogen creatinine ions and other types of waste products such as drugs.
Tubular secretion is the transfer of materials from peritubular capillaries to the renal tubular lumen and.