The walls of xylem vessels tracheids and sieve tubes are specialized for long distance transport. In the symplasmic route plasmodesmata PD the plant-specific microchannels penetrate cell walls thus providing a route for communication between cells.
In other words the primary purpose of plasmodesmata is to develop cell-to-cell communication in plants similar to gap-junction in animal cells.
Plasmodesmata function in plant cells. The plasmodesmata are tiny spaces in the cell wall through which cytosol can move from one cell to the next sharing organelles and nutrients. Plasmodesmata is the important Plasmodesmata transport water minerals and whatnot which could be said to be large molecules. The most important function of plasmodesmata is to connect cells together to facilitate water transport.
Plasmodesmata are cytoplasmic bridges through the cell wall connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells. Plasmodesmata in plant cell usually developed during cell division when the parts of the endoplasmic reticulum of the parent cell trapped by the new cell wall and get developed into daughter cells. The main function of plasmodesmata is to transverse the plant cell wall and allows to conduct and exchange the fluids between various cellular molecules between the plant cells.
Functions of Plasmodesmata. They are narrow channels that act as intercellular cytoplasmic bridges to facilitate communication and transport of materials between plant cells. In other words the primary purpose of plasmodesmata is to develop cell-to-cell communication in plants similar to gap-junction in animal cells.
They are also found in algae. Abundance in Plant Cells. Although they occur in varying numbers a typical plant cell has between 103 and 105 plasmodesmata distributed within 1 and 10 per µm 2.
Plasmodesmata represent one of the main cell-cell communication pathways in plant tissue. These structures also offer a channel for electrical signaling for the diffusion of lipids and small soluble molecules and even for the exchange of transcription factors and macromolecules such as. Plasmodesmata are intercellular pores connecting adjacent plant cells allowing membrane and cytoplasmic continuity and are essential routes for intercellular trafficking communication and signaling in plant development and defense Ganusova and Burch-Smith 2019.
PD establishes a direct connection of the plasma membrane endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasm between neighbor cells forming a. In plants cells are connected by symplasmic tunnels plasmodesmata PD. PD facilitate intercellular trafficking of essential molecules such as proteins sugars hormones and RNAs the movement of which is controlled by the permeability of PD to the molecule Zambryski 2008.
Answer 1 of 3. Plasmodesmeta are small pore like structure which connect two or more cells. They are small channels that directly connect the cytoplasm of neighboring plant cells to each other.
Plasmodesmata which penetrate both the primary and secondary cell walls allows certain molecules to. Intercellular transport in plants can also occur cytoplasm-to-cytoplasm through channels embedded in cell walls named plasmodesmata PD 5 6 7. These channels are membrane-continuous structures running across the cell walls of neighbouring cells arising primarily during cytokinesis.
The function of plasmodesmata. Plant cells are encased in cell walls that form the plant skeleton enabling and stabilizing three-dimensional growth. Just think what would celery be without plant cells walls.
However the presence of abundant extracellular cell wall material means that plant cells physically do not touch. The plasmodesmata help the plant cells communicate with each other. They facilitate the transport of small molecules like nutrients and other molecules that regulate plant growth as well as macromolecules like mRNA and proteins.
The transport is bidirectional meaning the molecules can move back and forth as required. Plasmodesmata is thin irregular cylinder of cytoplasm lined by plasmalemma passing through fine pores in the cell walls thus forming a connection between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells. They are found in higher plants and fluctuate widely in abundance and distribution.
Functions of cell wall. It gives definite shape to the cell. It protects the internal protoplasm against injury.
It gives rigidity to the cell. It prevents the bursting of plant cells due to endosmosis. The walls of xylem vessels tracheids and sieve tubes are specialized for long distance transport.
Plant intercellular communication occurs via symplasmic and apoplasmic pathways. In the symplasmic route plasmodesmata PD the plant-specific microchannels penetrate cell walls thus providing a route for communication between cells. PD allow trafficking of nutrients hormones and other informational molecules between neighboring cells and.
These strands are called plasmodesma connections or plasmodesmata. These connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells and facilitate the movement of substance between cells. Plasmodesmata are narrow channels through the wall bound by plasmalemmma containing cytoplasm and often a desmotubule.
Plasmodesmata PD are membrane-lined channels that transverse the plant cell wall and function as conduits to allow the exchange of various cellular molecules between plant cells1. The apposition between these two membranes constitutes a highly specialized type of. Plasmodesmata singular plasmodesma are small channels that directly connect the cytoplasm of neighboring plant cells to each other establishing living bridges between cells.
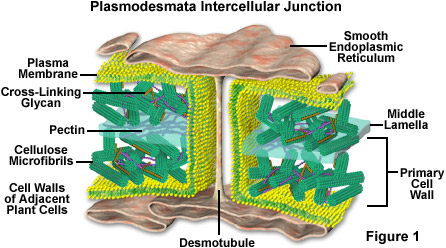
Similar to the gap junctions found in animal cells the plasmodesmata which penetrate both the primary and secondary cell walls see Figure 1 allow. Plasmodesmata are lined with cell membrane in effect uniting all connected cells with one continuous cell membrane cell. Plasmodesmata Similar to the gap junction of animal cells is the plasmodesma a channel passing through the cell wall and allowing direct.
In plants intercellular channels named plasmodesmata PD are formed consisting of a plasma membrane and an appressed ER desmotubule traversing cell walls Cheval and Faulkner 2018. These channels provide symplastic cytoplasm-to-cytoplasm connectivity between neighbouring cells through which transcription factors RNAs. But plasmodesmata provide plants with a unique means of intercellular communication whereby each plant cell has the ability to form direct conduits to its neighbors forming domains of cells sharing common cytoplasm.
Plasmodesmata serve as directors of plant growth and development and may help to determine a program of cell differentiation such as sealing off root and stem epidermal cells from the rest of.