
It converts food energy into chemical energy ATP with the help of oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondrion are organelles within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate ATP the main energy molecule used by the cell.
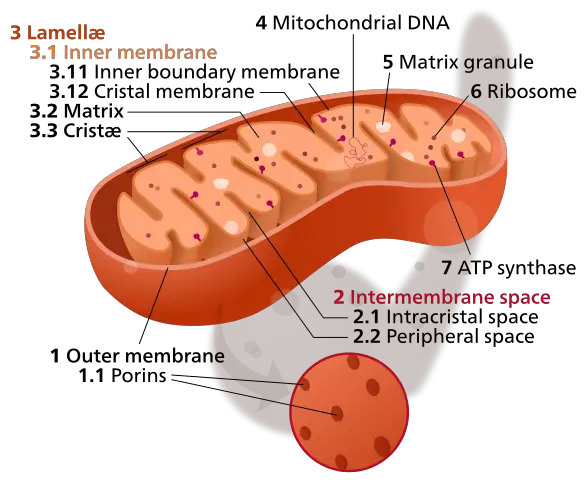
It is a double-membrane-bound organelle tiny organs within the cell.
Mitochondria definition and function. Mitochondrias primary function is to produce energy through the process of oxidative phosphorylation. Besides this it is responsible for regulating the metabolic activity of the cell. It also promotes cell multiplication and cell growth.
Mitochondria also detox ammonia in the liver cells. Mitochondrion are organelles within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate ATP the main energy molecule used by the cell. For this reason the mitochondrion is sometimes referred to as the powerhouse of the cell.
What Are Mitochondria. The mitochondrion plural mitochondria is a membrane-enclosed organelle responsible for the conversion of fats and carbohydrates into usable forms of energy for the body 1 2. The main function of the mitochondria is to produce ATP the main source of energy.
Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles mitochondrion singular that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cells biochemical reactions. Chemical energy produced by the mitochondria is stored in a small molecule called adenosine triphosphate ATP. Mitochondria contain their own small chromosomes.
The mitochondrion plural mitochondria is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is the power house of the cell. It is responsible for cellular respiration and production of most ATP in the cell.
Each cell can have from one to. Mitochondrion membrane-bound organelle found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells cells with clearly defined nuclei the primary function of which is to generate large quantities of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP. Mitochondria are typically round to oval in shape and range in size from 05 to 10 μm.
Mitochondria help decide which cells are destroyed. Mitochondria release cytochrome C which activates caspase one of the chief enzymes involved in destroying cells during apoptosis. Almost all eukaryotic cells required mitochondria for the production of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP an energy-rich molecule that powers basic cell processes.
Therefore known as the cells powerhouse. Mitochondria is a rod shaped membrane bound organelle that range in. Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell.
They are organelles that act as a digestive system which takes in nutrients breaks them down and creates energy-rich molecules for the cell. Krebs cycle fatty acid cycle electron transport system etc. Mitochondria are organelle present only in eukaryotic animals.
It is a double-membrane-bound organelle tiny organs within the cell. It contains an inner and outer layer. Moreover these layers are composed of phospholipids and proteins.
These are small 07 to 3 mm. Mitochondrion plural-mitochondria is a rounded rod-shaped or filamentous body. It is enclosed by double membrane.
The term mitochondria come from two Greek words such as mito and chondrion. In this case mito means thread while chondrion means granule. It is located in most of the cells and spreads all over the.
Mitochondria are the site of heat generation which is known as thermogenesis. Sometimes there can be the abnormal death of the cell. It might be due to the dysfunctioning of the mitochondria.
It can affect the function of the organ. It helps in the formation of some parts of the hormone of testosterone and estrogen. Mitochondria generate most of the cells supply of adenosine triphosphate used as a source of chemical energy.
They were first discovered by. Mitochondria are oxygen-consuming ribbon-shaped cellular organelles that float freely within the cell. They are called as the powerhouse of the cell because they provide all of the cells biological energy by oxidising the available substrates.
The mitochondrial enzymatic oxidation of chemical molecules releases energy. The two main functions of mitochondria are. 1 promoting the growth of new cells and in cell multiplication and 2 serving as the energy currency of the cell by synthesizing high-energy phosphate molecule ATP.
Controlling various cellular activities such as cell differentiation cell signaling cell movement and also in the cell cycle. Function in a Cell. The primary function is the creation of ATP via cellular respiration.
The mitochondria pick the nutrients of a cell and move them into energy through the form ATP. The higher energy a cell needs increases the number of mitochondria it would have. If a cell needs more energy than what is left it can make more as required.
The inner membrane of the mitochondria has characteristic folds called mitochondrial cristae. In this lesson discover the definition and function of the mitochondrial cristae. Mitochondria are organelles in eukaryotic cells that produce the chemical energy necessary to support biochemical reactions.
Explore the definition and functions of mitochondria. Mitochondria Definition Structure Composition Function Definition. Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles.
This organelle is also known as a powerhouse of cells. It converts food energy into chemical energy ATP with the help of oxidative phosphorylation. The ATP or chemical energy known as Adenosine Triphosphate ATP.
Mitochondria are oxygen-consuming ribbon-shaped cellular organelles of immense importance floating free throughout the cell. They are known as the powerhouse of the cell since these organelles supply all the necessary biological energy to the cell by oxidizing the substrates available.