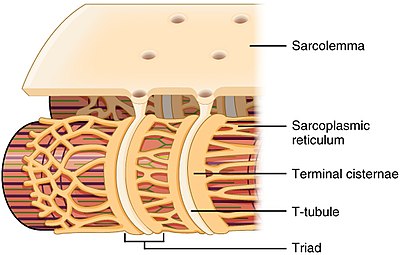
T-tubules are invaginations of the plasma membrane which are present exclusively in striated muscle. The function of T-TUBULES is to conduct impulses from the surface of the cell SARCOLEMMA down into the cell and specifically to another structure in the cell called the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM.
The primary duty of transverse tubules or T-tubules is to allow the conduction of electrical impulses.
Function of t tubules. The primary duty of transverse tubules or T-tubules is to allow the conduction of electrical impulses. Transverse tubules exist as invaginations of sarcolemma which are muscle fiber membranes. Transverse tubules comprise a triad along with two parallel strands of sarcoplasmic reticulum which varies in size and shape depending on muscle cell.
The function of T-TUBULES is to conduct impulses from the surface of the cell SARCOLEMMA down into the cell and specifically to another structure in the cell called the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. The t-tubules are also known as transverse tubules. These are the organelles present as the extensions of the plasma membrane in the striated muscle cells.
The function of T-TUBULES is to conduct impulses from the surface of the cell SARCOLEMMA down into the cell and specifically to another structure in the cell called the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. The most recognized function of t-tubules is regulation of cardiac EC coupling by concentrating voltage-gated L-type calcium channels LTCCs and positioning them in close proximity to calcium sense and release channels ryanodine receptors RyRs at the junctional membrane of sarcoplasmic reticulum jSR. The function of the t-tubules depends not only on their structure but also on the proteins within and adjacent to the t-tubule membrane.
Immunohistochemical techniques have been widely used to investigate the location of proteins within cardiac ventricular myocytes. The function of T-TUBULES is to conduct impulses from the surface of the cell SARCOLEMMA down into the cell and specifically to another structure in the cell called the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. By differentially compartmentalizing proteins involved in ion handling and signaling T-tubules serve as a signaling hub-like organelle to regulate the myocyte function.
The expression of transmembrane ion channels ion transporters and pumps have been well characterized in cardiac T-tubules. In cardiac muscle the transverse or T-tubules penetrate the muscle cell interior at the level of the Z line so that cardiac muscle has only one T-tubule per sarcomere. The sarcoplasmic reticulum or SR membrane is a membranous network that surrounds the myofibrils and makes contact with the T-tubule at junctions called dyads.
These channels are called the transverse tubules T tubules because they run across the fibre. The transverse tubular system is a network of interconnecting rings each of which surrounds a myofibril. It provides an important communication pathway between the outside of the fibre and the myofibrils some of which are Read More.
T tubules propagate the action potential from the plasma membrane into the interior of the muscle cell via voltage-gated Na and K channels 2. An action potential carried by a T tubule regulates the opening and closing of Calcium channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The most recognized function of t-tubules is regulation of cardiac EC coupling by concentrating voltage-gated L-type calcium channels LTCCs and positioning them in close.
The most recognized function of t-tubules is regulation of cardiac EC coupling by concentrating voltage-gated L-type calcium channels LTCCs and positioning them in close proximity to calcium sense and release channels ryanodine receptors RyRs at the junctional membrane of sarcoplasmic reticulum jSR. Tubulus T tubulus transversal atau T-tubule transverse tubules adalah invaginasi dari membran eksternal sel otot rangka dan jantung yang kaya akan saluran ion yang penting untuk perpasangan eksitasi-kontraksi. Calcium channels ryanodine receptors are located at the points of contact of the T- tubules with the SR.
When T- tubes are depolarized they open and calcium ions leave the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber. Previously it was believed that there is a protein domain between the calcium channels and the T- tube membrane which provides mechanical coupling of. T-tubules are invaginations of the plasma membrane which are present exclusively in striated muscle.
Their role is to maintain the SR calcium store under the tight control of membrane depolarization via the voltage sensor channel DHPR. Thus the t-tubules are an important determinant of cardiac cell function especially as the main site of excitation-contraction coupling ensuring spatially and temporally synchronous Ca 2. T-tubules are critical for several aspects of muscle contractions and force generation in particular for excitation-contraction coupling.
Impairment of this network should clearly lead to diminished force production and muscle weakness.