
The renal cortex is the part of the kidney where ultrafiltration of blood takes place. It is a thick layer of fatty tissues.
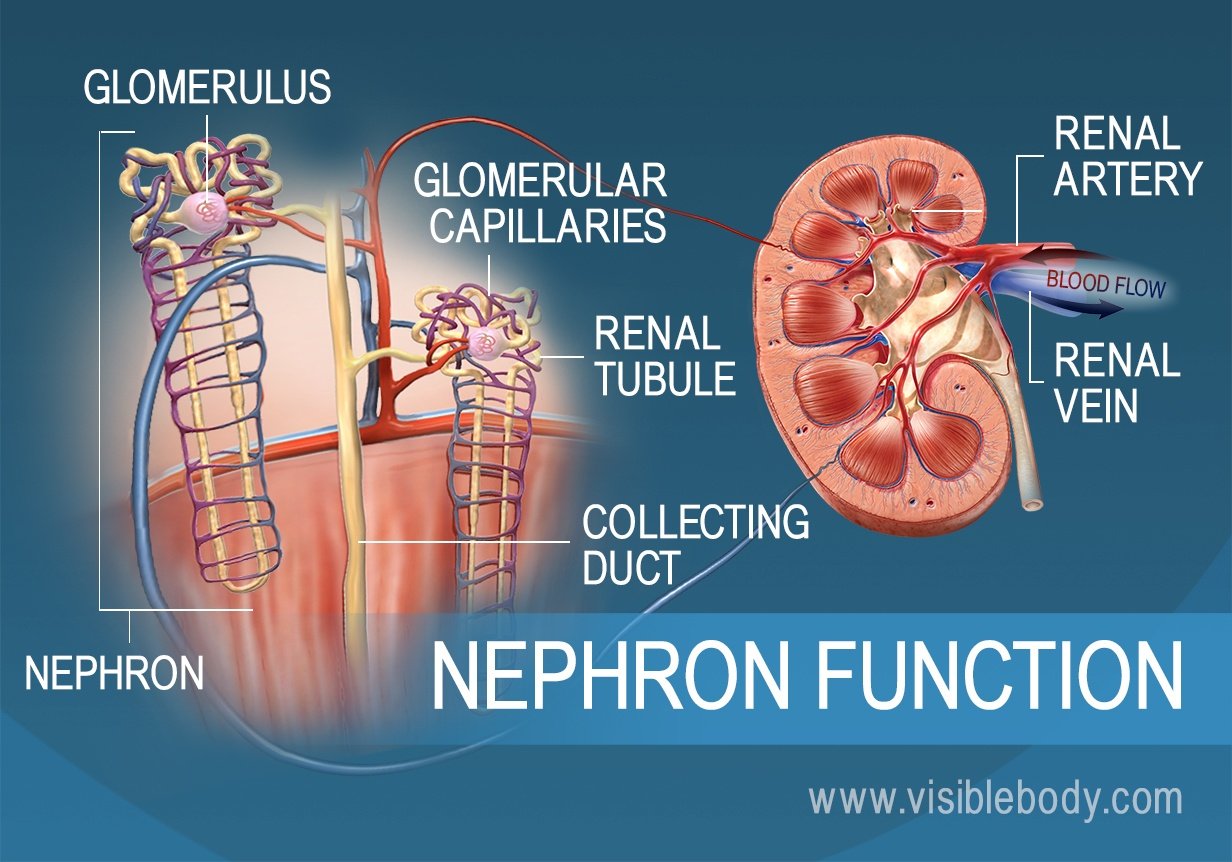
Parts of the kidney and their functions.
Function of kidney cortex. Between the glomerulus blood vessels and Bowmans space there is a filtration membrane which helps to keep cells and proteins from leaving the glomerulus. The process occurring in the renal cortex is sometimes referred to as ultrafiltration and the water and molecules in. The cortex provides a space for arterioles and venules from the renal artery and vein as well as the glomerular capillaries to perfuse the nephrons of the kidney.
Erythropotein a hormone necessary for the synthesis of new red blood cells is also produced in. Cortex The outer region of the kidney. Extensions of the cortical tissue contains about one million blood filtering nephrons Nephron these are the filtration units in the kidneys Medulla the inner region of the kidney contains that contains 8-12 renal pyramids.
The cortex of the kidney is the second site of the enzyme arginase in the body. The major function of this enzyme is the synthesis of the precursor of creatine guanidinoacetic acid. When endogenous nonhepatic proteins are hydrolyzed there is a steady release of their constituent amino acids including arginine into the systemic circulation throughout the 24-hour period.
People typically have two kidneys and their basic function is to filter the blood and remove waste products inside the body. The cortex is usually thought of as a sort of an insulation layer. It isnt the outermost covering but it isnt really in the middle either.
The cortex provides a space for arterioles and venules from the renal artery and vein as well as the glomerular capillaries to perfuse the nephrons of the kidney. Erythropotein a hormone necessary for the synthesis of new red blood cells is also produced in the renal cortex. Click to see full answer.
Similarly one may ask what does the cortex. Function in kidneysomewhat granular outer section the cortex containing the glomeruli and convoluted tubules and a smooth somewhat striated inner section the medulla containing the loops of Henle and the collecting tubules. As the ureter enters the kidney it enlarges into a cavity the renal pelvis.
Urine passes into this pelvis from. Its main functions are. Filter reabsorb substances and secrete.
It is the deepest part. It is located after the renal cortex. It is composed by 8-18 renal pyramids cone-shaped tissues also called Malpighis pyramids among which are the columns of Bertin.
The pyramids are separated by extensions of the cortex called the renal columns. The pyramids contain the functional units of the kidney the nephrons which filter blood in order to produce urine which then is transported through a system of the structures called calyces which then transport the urine to the ureter. So the pyramids represent the functional tissue that creates urine whereas the.
The renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney between the renal capsule and the renal medulla. In the adult it forms a continuous smooth outer zone with a number of projections cortical columns that extend down between the pyramidsThe renal cortex is the part of the kidney where ultrafiltration occurs. The other part of the kidney is called the renal cortex which contains convoluted tubules and glomerulus.
It is surrounded by a renal capsule on its outer edges. It is a thick layer of fatty tissues. The renal cortex along with the help of the capsule house protects the inner structure of the kidney.
Regulating and filtering minerals from blood. Filtering waste materials from food medications and toxic substances. The Functional Unit of Kidney.
The nephron is the kidneys functional unit that removes waste from the body. Each kidney has more than a million nephrons in the renal cortex which gives it a granular appearance on sagittal section. There are 2 types of nephrons.
Each of the renal lobes contains the renal cortex which surrounds a portion of the medulla called the renal pyramid. Between the renal pyramids there are projections of the cortex called renal columns. Nephrons are the urine-producing functional structures of.
The renal cortex is granular tissue due to the presence of nephronsthe functional unit of the kidneythat are located deeper within the kidney within the renal pyramids of the medulla. The cortex provides a space for arterioles and venules from the renal artery and vein as well as the glomerular capillaries to perfuse the nephrons of the kidney. Erythropotein a hormone necessary for the.
The cortex also extends between medulla regions to form sections known as renal columns. The renal pelvis is the area of the kidney that collects the urine and passes it to the ureter. Nephrons are the structures that are responsible for filtering blood.
The renal cortex is the part of the kidney where ultrafiltration of blood takes place. The blood flows into the glomerular capillaries in the Bowmans capsule. Function Renal cortex involves in urine dilation.
Renal medulla involves in urine concentration. Erythropoietin Renal cortex is the site of erythropoietin production. Renal cortex the granular outer layer of the kidney composed mainly of glomeruli and convoluted tubules extending in columns between the pyramids that constitute the renal medulla.
Striate cortex part of the occipital lobe that receives the fibers of the optic radiation and. The reptilian renal cortex contains only simple nephrons cortical nephrons that have a tubular system devoid of loops of Henle. Therefore reptiles are unable to concentrate their urine.
Nitrogenous wastes excreted by the reptilian kidney include variable amounts of uric acid urea and ammonia depending on the animals natural environment. Parts of the kidney and their functions. Each kidney is composed of three sections the outer cortex the medulla and the hollow inner pelvis where urine accumulates before it travels down the ureters.
Within the cortex and medulla of each kidney are about one million tiny filters called nephrons. Each nephron consists of five parts. The renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney between the renal capsule and the renal medulla.
In the adult it forms a continuous smooth outer zone with a number of projections cortical columns that extend down between the pyramidsThe renal cortex is the part of the kidney where ultrafiltration occurs.