
It provides cells with the energy they need to function. Cellular respiration does not always require oxygen but aerobic cellular respiration is more efficient and produces more.
The Cellular Respiration Process The metabolism of glucose to yield energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP and CO2 carbon dioxide a waste product in this equation is known as cellular respiration.
Function of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the cellular process which transfers chemical energy from glucose to ATP. Oxygen is essential to have efficient cellular respiration. Most organisms need oxygen for a single purpose.
To release energy from food for use by cells. What is cellular respiration and what is its primary function. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells in plants and animals break down sugar and turn it into energy which is then used to perform work at the cellular level.
The purpose of cellular respiration is simple. It provides cells with the energy they need to function. What is the major function of cellular respiration.
The main function of cellular respiration is to synthesize biochemical energy. Cellular respiration is essential to both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells because this biochemical energy is produced to fuel many metabolic processes such as biosynthesis locomotion and transportation of molecules across membranes. Cellular respiration involves catabolic reaction in order to break down food into usable energy so that cells and the living organisms that contain them can survive and thrive.
Cellular respiration is the process by which food in the form of sugar glucose is transformed into energy within cells. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a.
The main function of cellular respiration is to break down molecules and generate ATP. What is the primary purpose of cellular respiration. The primary purpose of cellular respiration is to produce ATP as needed for cells.
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or. The function of cellular respiration is to _____.
Extract usable energy from glucose –The most prevalent and efficient energy-yielding pathway is cellular respiration in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel frequently glucose–. Steps of Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is an oxidative process where glucose gets converted into carbon dioxide yielding ATP and NADHFADH 2.
The process takes place in four stages. Also known as the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway it is. Cellular respiration is the process that cells use to make energy.
Cellular respiration does not always require oxygen but aerobic cellular respiration is more efficient and produces more. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism.
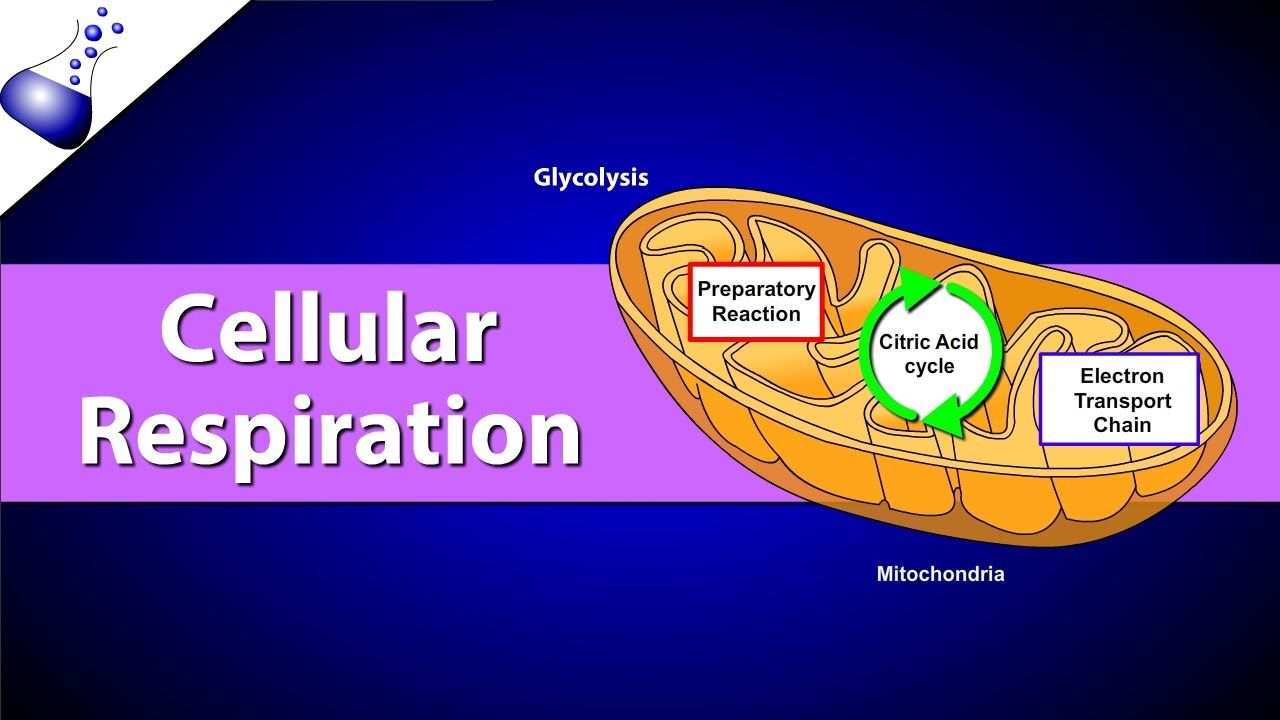
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages. Glycolysis the Krebs cycle and electron transport. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process.
The other two stages are aerobic processes. The products of cellular respiration are needed for photosynthesis and vice versa. The term cellular respiration refers to the biochemical pathway by which cells release energy from the chemical bonds of food molecules and provide that energy for the essential processes of life.
All living cells must carry out cellular respiration. It can be aerobic respiration in the presence of oxygen or anaerobic respiration. Cellular respiration can proceed in the absence of oxygen but it looks pretty different after glycolysis.
If oxygen isnt present some organisms like many gut bacteria can undergo anaerobic without oxygen fermentation. This is the source of much intestinal gas. Chapter 8 Section 3.
What Is The Function Of Cellular Respiration. The role of cellular respiration is to convert glucose into readily available energy. Using Words Only Write The Chemical Equation For Cellular Respiration.
Glucose Oxygen Carbon dioxide. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. The Cellular Respiration Process The metabolism of glucose to yield energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP and CO2 carbon dioxide a waste product in this equation is known as cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration is a very important metabolic process that occurs in all living organisms. The process converts the organic molecules into ATP. ATP is the energy molecule for all living organisms therefore this process has great significance.
It takes place in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Pyruvate and cellular respiration. Pyruvate molecules are formed during a series of important reactions called glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the breakdown pathway for glucose molecules and the first step in cellular respiration. Glycolysis is the complete opposite of gluoconeogenesis because a 6-carbon molecule breaks down into two 3-carbon compounds.