Describe the structure of sarcomere. Their specific arrangement helps these small units to coordinate the contractions of our muscles.

By contraction in unison Sarcomeres may trigger broad sweeping motions.
Describe the structure of a sarcomere. A sarcomere is the functional unit of striated muscle. This means it is the most basic unit that makes up our skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type that initiates all of our voluntary movement.
Herein lies the sarcomeres main purpose. Sarcomeres are able to initiate large sweeping movement by contracting in unison. Sarcomere are the basic unit of striated muscle tissue.
It forms the repeating unit between two Z lines. Skeletal muscles is made up of tubular muscle cells. Each muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils.
The myofibrils consists of repeating sections of. A sarcomere is closed on both sides by what is known as a Z line. This serves as an attachment point for the thin filament actin which extends into.
See full answer below. A sarcomere describes as the distance between two Z discs or Z lines. When a muscle contracts in our body the distance reduces between the Z discs.
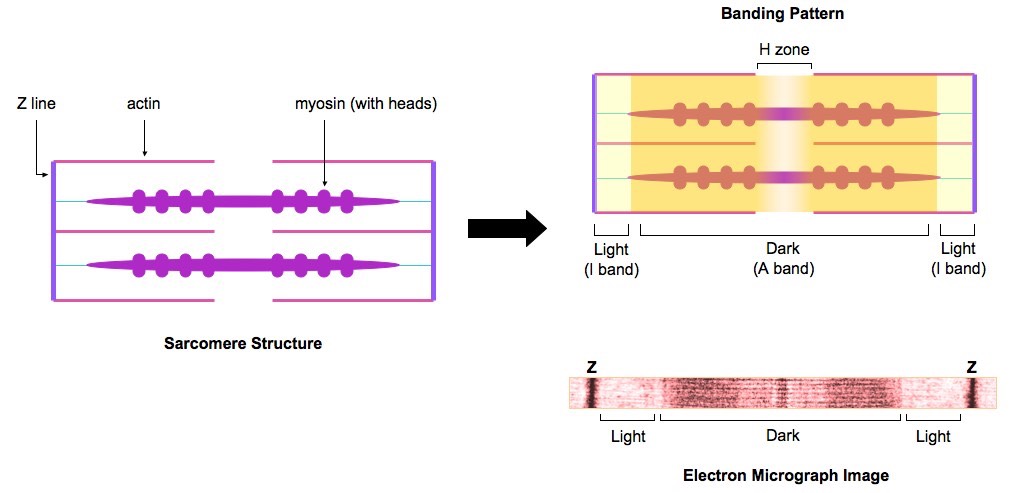
The central region of the A zone H zone contains only thick filaments myosin and became short during contraction. The sarcomere is termed as a basic unit of striated muscle tissue and skeletal muscles are made of tubular muscle cells myocytes and myofibrils of muscle fibers and are developed by. Each sarcomere consists of thick thin beams of the proteins mentioned above which together are called myofilaments.
By expanding a portion of the myofilaments you can identify the molecules that make them up. Describe and diagram the structure of a sarcomere and the primary components of the thick and thin filament. Skeletal muscles are organized into compact layers of.
Describe the structure of sarcomere. They are highly organised within skeletal and cardiac muscle which give a stripedstriated appearance to the muscle. A sarcomere is the portion of a myofibril that lies between two successive Z disks.
A sarcomere consists of a dark band in the centre and light bands on either side. The dark band or Anisotropic band A band is made of myosin and the light band on Isotropic band I- band is made of actin filaments. Describe the structure of sarcomere.
By contraction in unison Sarcomeres may trigger broad sweeping motions. Their specific arrangement helps these small units to coordinate the contractions of our muscles. The contractile characteristics of muscle are in general a distinguishing function of animals.
The Basic Contractile Unit of Muscle. A sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber. Each sarcomere is composed of two main protein filamentsactin and myosinwhich are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction.
2 Describe the microscopic structure of a skeletal muscle sarcomere and motor unit -consists of numerous thick and thin filaments arranged so that dark and light stripes cross striations are seen 3 Briefly describe the structure of cardiac muscle. A sarcomere is defined as the region of a myofibril contained between two cytoskeletal structures called Z-discs also called Z-lines and the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement of the thick and thin myofilaments within each sarcomere Figure 1022. The sarcomere is the basic contractile unit for both striated and cardiac muscle and is made up of a complex mesh of thick filaments thin filaments and a giant protein titin.
Cellular and Molecular Pathobiology of Cardiovascular Disease 2014. Cytoplasm large numbers of mitochondria packed between myofibrils to perform aerobic respiration and produce ATP required for muscle contraction. Cell surface has large numbers of protein pumps to transport Ca2 into cisternae of SR.
A sarcomere Greek σάρξ sarx flesh μέρος meros part is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells called muscle fibers or myofibers which are formed during embryonic myogenesis.
Sarcomere a molecular structure in myofibrils that allows cardiac myocytes to contract and generate force. Watch location of the sarcomere video Sarcomere Components. The structure of the sarcomere is organized into bands of interdigitating thick filaments and thin filaments.
Thick filaments attach to the middle of the sarcomere or M line and. Describe the structure of the sarcomere and explain how it enables muscle contraction according to the sliding-filament model. Start your trial now.
First week only 499. Describe the structure of striated muscle fibers including the myofibrils with light and dark bands mitochondria the sarcoplasmic reticulum nuclei and the sarcolemma. Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere including Z lines actin filaments myosin filaments with heads and the resultant light and dark bands.
Sarcomere A portion of myofibril that lies between two successive Z discs is called sarcomere. Sarcomere ½ I band A band ½ I band. The structural functional unit of muscle fiber.
LONG ESSAY Describe the molecular structure of contractile proteins in skeletal muscle. Discuss the mechanism of contraction. Draw diagrams to compare the Sarcomere at rest and during contraction.
Describe the organization and function of Sarcotubular system in the skeletal muscle. SHORT ANSWER Explain what is relaxing protein in skeletal muscle.