All enzymes for the krebs cycle are in the matrix ensuring high enzyme concentration and reduced loss of intermediates. In cells such as muscle it is clear that mitochondria are not spherical and often are not even ellipsoid.
In cells such as muscle it is clear that mitochondria are not spherical and often are not even ellipsoid.
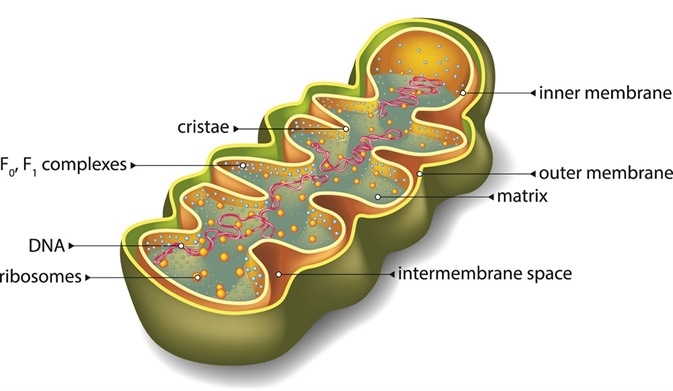
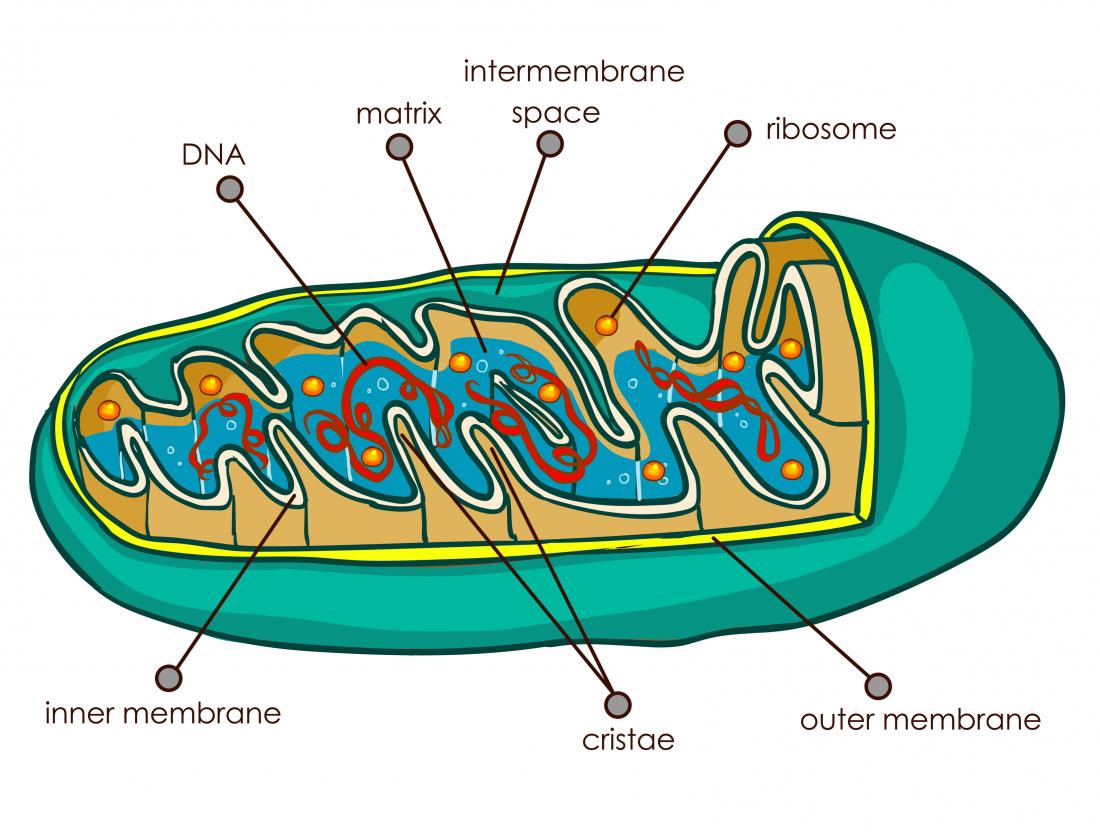
Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. The mitochondrion is a double-membraned rod-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cell. Its size ranges from 05 to 10 micrometre in diameter. The structure comprises an outer membrane an inner membrane and a gel-like material called the matrix.
Mitochondria in situ can be free in the cytoplasm or packed in among more rigid structures such as among the myofibrils of cardiac muscle tissue. In cells such as muscle it is clear that mitochondria are not spherical and often are not even ellipsoid. Mitochondria have an inner and outer membrane with an intermembrane space between them.
The outer membrane contains proteins known as porins which allow movement of ions into and out of the mitochondrion. Enzymes involved in the elongation of fatty acids and the oxidation of adrenaline can also be found on the outer membrane. Mitochondria are enclosed by two membranesa smooth outer membrane and a markedly folded or tubular inner mitochondrial membrane which has a large surface and encloses the matrix space.
The folds of the inner membrane are. Usually mitochondria are 05 to 1 n in diameter and 3-6n in length. They however vary in their size and are also capable of changing their size.
They are generally rod shaped but may be in the form of granules or spherical bodies. Their number may vary from 50 to 50000 in different kinds of cells. The mitochondrion is a rod-shaped double membraned organelle.
The inner membrane and outer membrane are separated by the intermembrane space. The outer membrane is smooth while the inner membrane is convoluted with infoldings known as the cristae. A mitochondrion is a round to oval-shaped organelle found in the cells of almost all eukaryotic organisms.
It produces energy known as ATP for the cell through a series of chemical reactions. Explain how the structure of the mitochondria relates to its function. The mitochondria has three key parts matrix inner membrane and outer membrane.
The matrix is the internal space where the krebs cycle takes place. All enzymes for the krebs cycle are in the matrix ensuring high enzyme concentration and reduced loss of intermediates. Each mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound structure.
Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell as they produce cellular energy in the form of ATP to keep the individual cells and the plant functioning. Structure of Mitochondria.
Mitochondria are mobile plastic organelles that have a double-membrane structure. It ranges from 05 to 10 micrometer in diameter. It has four distinct domains.
The outer membrane the inner membrane the intermembrane space and the matrix. The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell ATP and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur. Structure Mitochondria is about 1 mm in diameter and 1-10 mm in length.
A detailed look at the structure of the mitochondrion helps to explain its role in the last stage of respiration the electron transport chain. Mitochondrion are sometimes referred to as the. Mitochondria in animals is round or oval in shape and is bound by a double membrane.
These membranes are composed of phospholipid bilayers and proteins. The different parts of mitochondria in animal cell are. A Outer membrane- The outer membrane keeps the inner organelles intact and in place.
A mitochondrion contains outer and inner membranes composed of phospholipid bilayers and proteins. The two membranes have different properties. Because of this double-membraned organization there are five distinct parts to a mitochondrion.
The outer mitochondrial membrane The intermembrane space the space between the outer and inner membranes. 21 is an electron micrograph showing the main structural features of a mitochondrion in section. 21 a Indicate clearly on the diagram where.
I oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Ii Krebs cycle occurs. 2 b Describe two ways in which the structure of the mitochondrion is adapted for oxidative phosphorylation.
Mitochondria are ovoid rounded rod shape and pleomorphic structures. Mitochondrion consists of double membrane the outer and inner membrane. The outer membrane is smooth highly permeable to small molecules and it contains proteins called Porins which form channels that allows free diffusion of molecules smaller than about 1000 daltons and the.