The primary function of mitochondria is to provide the energy required for various cellular activities most significantly the formulation of energy. Distribution Morphology Functions and Origin of Mitochondria.
Cells which are very metabolically active such as hepatocytes will have many mitochondria.
Describe the function of mitochondria. Mitochondrias primary function is to produce energy through the process of oxidative phosphorylation. Besides this it is responsible for regulating the metabolic activity of the cell. It also promotes cell multiplication and cell growth.
Mitochondria are a part of eukaryotic cells. The main job of mitochondria is to perform cellular respiration. This means it takes in nutrients from the cell breaks it down and turns it into energy.
This energy is then in turn used by the cell to carry out various functions. Each cell contains a. Those membranes function in the purpose of mitochondria which is essentially to produce energy.
That energy is produced by having chemicals within the cell go through pathways in other words be converted. And the process of that conversion produces energy in the form of ATP because the phosphate is a high-energy bond and provides energy for. What Is the Function of the Mitochondrion.
A mitochondrion produces energy for a cell. Mitochondria the plural of mitochondrion are small organelles found in most nucleated cells including those of plants animals and fungi. The primary mechanism by which mitochondria generate energy is through the manufacture of ATP.
The main function of mitochondria is the production of ATP through cellular respiration. Other functions of mitochondria include heat production programmed cell death regulation of the metabolic activity in a cell and the storage of calcium. When mitochondria produce ATP they.
Mitochondria have many other functions as well. They can store calcium which maintains homeostasis of calcium levels in the cell. They also regulate the cells metabolism and have roles in apoptosis controlled cell death cell signaling and thermogenesis heat production.
The most important function of the mitochondria is to produce energy. The simpler molecules of nutrition are sent to the mitochondria to be processed and to produce charged molecules. These charged molecules combine with oxygen and produce ATP molecules.
This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondria are integral to normal cellular function as they are responsible for energy production in eukaryotes including the synthesis of phospholipids and heme calcium homeostasis apoptotic activation and cell death. 12 Alterations in mitochondrial function often associate with disease states including endocrine related disorders such as diabetes mellitus reflecting the.
Discover the importance and function of a mitochondrions inner membrane ATP and the electron transport chain. The prime function of mitochondria is to produce energy. It is the power generation plant where the nutrients turn into ATP by a chemical process.
The other major roles played by mitochondria are carrying out cellular metabolism. Function The mitochondrion is the site of ATP synthesis for the cell. The number of mitochondria found in a cell are therefore a good indicator of the cells rate of metabolic activity.
Cells which are very metabolically active such as hepatocytes will have many mitochondria. Mitochondrion organelle found in most eukaryotic cells the primary function of which is to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate. Mitochondria also store calcium for cell signaling activities generate heat and mediate cell growth and death.
They typically are round to oval in shape. Mitochondria singular mitochondrion are often called the powerhouses or energy factories of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate ATP the cells main energy-carrying molecule. The formation of ATP from the breakdown of.
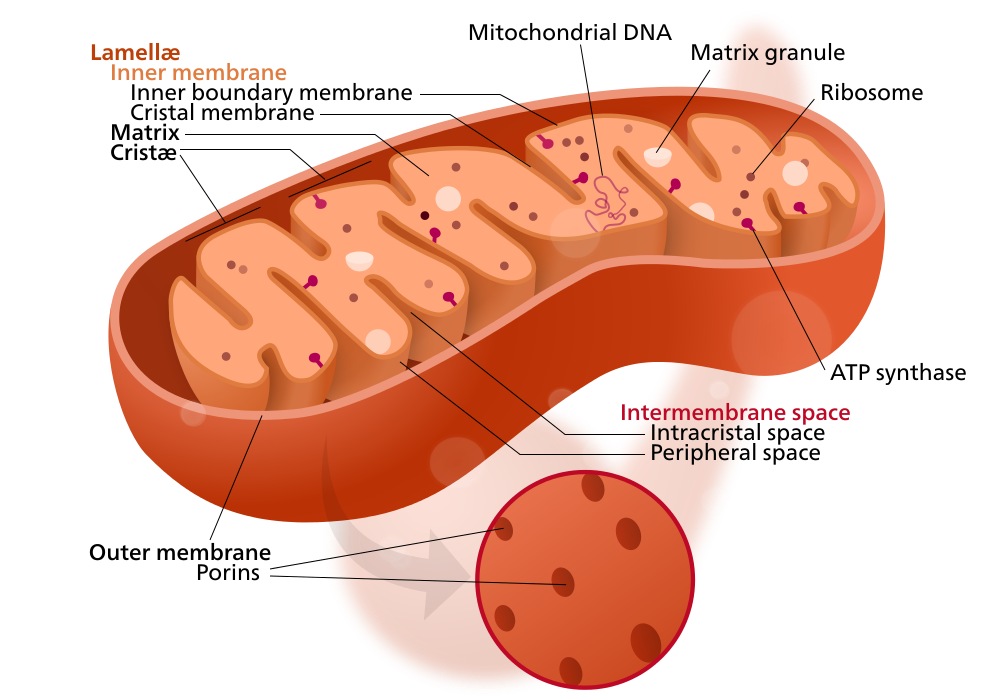
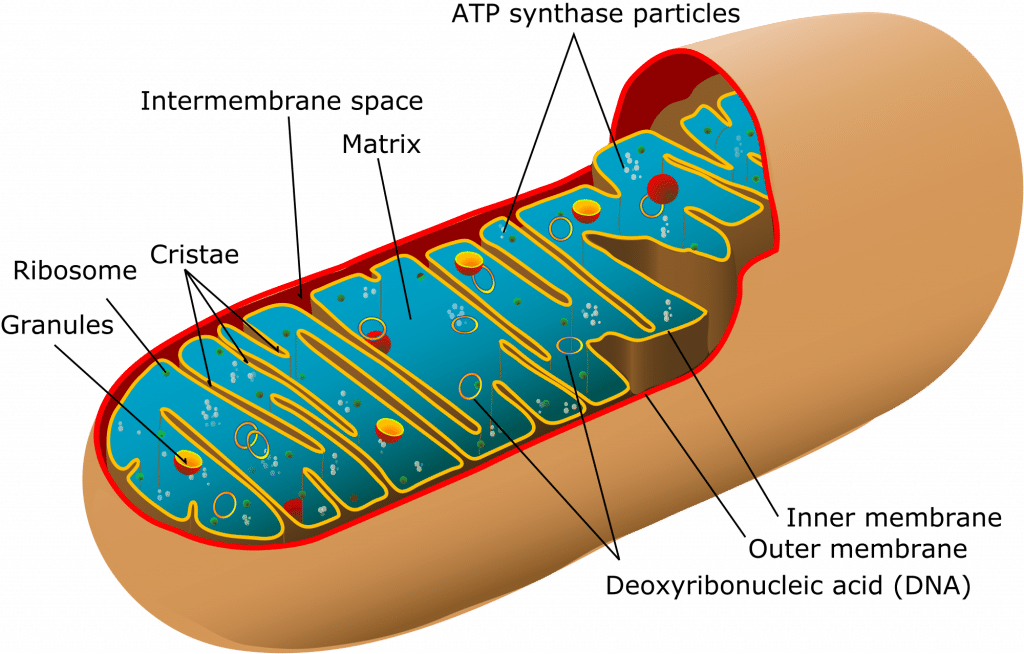
MITOCHONDRIA THEIR STRUCTURE FUNCTIONS AND DISEASES LINKED TO THE ORGANELLE. Part 1The structure of mitochondria. Morphology and organelle interactions.
The fusion fission cycle of mitochondria. Functions of Mitochondria. The major function of the mitochondria is to produce energy.
The energy giving food molecule are sent to the mitochondrion where they are further precessed to produce charged molecules that combine with oxygen and produce ATP molecules. Though the primary function of mitochondria is to produce energy they also play an important role in the metabolism and synthesis of certain other substances in the body. Structure and Functions Mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cells.
Distribution Morphology Functions and Origin of Mitochondria. Kоlliker 1880 was the first who observed the granules mitochondria in muscle cell of insects. Flemming 1882 named the mitochondria as fila.
Altmann in 1894 observed them and they were called Altmanns granules bioplasts. The term mitochondria were applied by Benda. Organelles found in eukaryote cells.
They are the sites of the link reaction Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation - the aerobic stage of respiration. What is the range in diameter of mitochondria. What is the range in length of mitochondria.
Mitochondria is regarded as the power house of the cell as it is the site of respiration. The general formula for glucose oxidation is. The mitochondria plural mitochondria is a membrane bound structure found in both eukaryotic plant and animal cells.
The primary function of mitochondria is to provide the energy required for various cellular activities most significantly the formulation of energy.