The process of phagocytosis often happens when the cell is trying to destroy something like a virus or an infected. Phagocytosis is a specialized process by which cells engulf relatively large solid material.

Eg White blood cells are Phagocytes first line of defence.
Define phagocytosis in biology. Phagocytosis refers to the process by which certain living cells called phagocytes engulf other cells particles and even pathogens. Phagocytosis process occurs when the cell tries to destroy foreign particles or pathogens such as bacteria or an infected cell by engulfing it. Phagocytosis or cell eating is the process by which a cell engulfs a particle and digests it.
The word phagocytosis comes from the Greek phago- meaning devouring and -cyte meaning cell. Cells in the immune systems of organisms use phagocytosis to devour bodily intruders such as bacteria and they also engulf and. Phagocytosis is a specific form of endocytosis by which cells internalise solid matter including microbial pathogens.
While most cells are capable of phagocytosis it is the professional phagocytes of the immune system including macrophages neutrophils and mmature dendritic cells that truly excel in. Phagocytosis process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles. The phagocyte may be a free-living one-celled organism such as an amoeba or one of the body cells such as a white blood cell.
In some forms of animal life such as amoebas and sponges phagocytosis is a. Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis a process through which a cell consumes material by engulfing it with its membrane. Phagocytosis is the engulfing of large particles such as entire cells.
Phagocytosis is a process wherein a cell binds to the item it wants to engulf on the cell surface and draws the item inward while engulfing around it. The process of phagocytosis often happens when the cell is trying to destroy something like a virus or an infected. Essentially phagocytosis may be described as a form of endocytosis through which a cell engulfs particulate mattersolid particlescells.
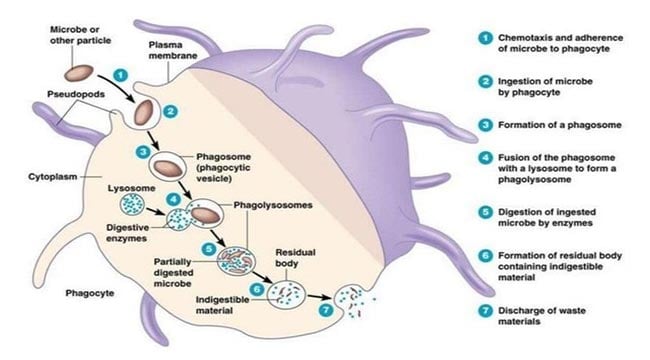
For different types of cells phagocytosis plays a number of different roles ranging from food ingestion to the destruction of given cells and particulate matter. Phagocytosis is one of the most important process of our bodys first line defence though which the microbes that entered into our body are engulfed and destroyed by some particular immune cells. They are engulfed into a large vesicle of the cells through endocytosis.
The cells that perform that process called phagocytes. Phagocytosis is the most important process of our innate. Phagocytosis is the process in which most WBCs and particularly the neutrophils engulf particle-like solid substances especially bacteria.
Phagocytosis or Phagocytic barrier of immune system. Phagocytosis is an important defense mechanism of host to provide immunity. Most of the bacteria that enter into host are killed by phagocytic cells such as Neutrophils monocytes and macrophages.
The process of ingestion of solid substances eg. Cells bacteria parts of necrosed tissue by cells and transported to a site within the cell where it. Phagocytosis is a nonspecific defense mechanism in which various phagocytes engulf and destroy the microorganisms of disease.
Among the important phagocytes are the circulating white blood cells called neutrophils and monocytes. In the tissues the monocytes are transformed into phagocytic cells called macrophages. Phagocytosis from Ancient Greek φαγεῖν phagein to eat and κύτος kytos cell is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle 05 μm giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome.
Phagocytosis definition the ingestion of a smaller cell or cell fragment a microorganism or foreign particles by means of the local infolding of a cells membrane and the protrusion of its cytoplasm around the fold until the material has been surrounded and engulfed by closure of the membrane and formation of a vacuole. Characteristic of amebas and some types of white blood cells. Phagocytosis is the cellular process of phagocytes and protists of engulfing solid particles by the cell membrane to form an internal phagosome.
Phagocytosis is a specific form of endocytosis involving the vesicular. Full article process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles. The phagocyte may be a free-living one-celled organism such.
What is phagocytosis. Phagocytosis is a specialized process by which cells engulf relatively large solid material. Unicellular organisms such as amoebas use phagocytosis to acquire nutrition while cell types of multicellular organisms use this universal process for preventative functions such as tissue homeostasis.
Phagocytosis non specific defence mechanism the engulfing of cells in the form of vesicles formed from the cell-surface membrane. Eg White blood cells are Phagocytes first line of defence. Niedergang in Encyclopedia of Cell Biology 2016 Introduction.
Phagocytosis is a universal cell function which starts with the recognition and binding of a particle over 05 µm in diameter generally in a receptor-dependent manner and leads to its internalization and degradation. Single-celled eukaryotes such as the mold Dictyostelium discoideum and amoebae use phagocytosis for feeding. Phagocytosis is an intake of solid particles with the formation of vesicles called phagosomes while pinocytosis is the intake of liquid particles with the formation of vesicles called pinosomes.
The term Endocytosis was given by Christain de Duve in the year 1963. Cytoplasmic fragments of large cells produced by bone marrow. 1 cutpuncture in skin.
2 blood therefore platelets ooze out. Part of immune system destroy pathogens bacteriavi. 1 phagocyte recognises antigens on a.
Phagocytosis Also known as cell eating. When a cell absorbs large particles such as whole bacteria. Invagination The process by which a structure in this case the cell membrane is folded back or turned inside out to form a pocket or cavity.
Phagocyte definition any cell as a macrophage that ingests and destroys foreign particles bacteria and cell debris.