Bacterium are prokaryotic generally unicellular organisms which exist as single cells or as cell clusters. Bacteria that produce toxins are said to be toxigenic in nature.
Bacteria display an array of contact-dependent interaction systems that have evolved to facilitate direct cell-to-cell communication.
Characteristics of bacterial cells. Bacterial cell characteristics are much like those of eukaryotic cells but simpler. Critically bacterial cells have cell walls in addition to a cell membrane. Their DNA resides in the cytoplasm rather than inside a nucleus and bacteria lack organelles.
They usually reproduce asexually. What is Bacteria. Bacteria are disease-causing microscopic single-celled organisms with prokaryotic cell structures.
They do not have membrane-bound organelles including a true nucleus. Being the lowest and simplest form of life they are found almost everywhere on earth and thus are the most dominant living creature. 32 A Typical Bacterial Cell 1.
Distinguish a typical bacterial cell from a typical plant or animal cell in terms of cell shapes and arrangements size and cell structures 2. Discuss the factors that determine the size and shape of a bacterial cell. All bacteria both pathogenic and saprophytic are unicellular organisms that reproduce by binary fission.
Most bacteria are capable of independent metabolic existence and growth but species of Chlamydia and Rickettsia are obligately intracellular organisms. Bacterial cells are extremely small and are most conveniently measured in microns 10-6 m. They range in size from large cells such as.
Bacterium are prokaryotic generally unicellular organisms which exist as single cells or as cell clusters. They are among the organisms that are too small to be visible to the naked eye. Thus they can only be seen with the aid of a microscope.
Bacteria are all single-celled. The cells are all prokaryotic. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes.
Larger bacterial cells may be. Discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components 4. Discuss the distinguishing characteristics of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.
For this lecture you should focus on the major concepts and not on the names of the different bacteria. They are mentioned as illustrations of different principles. The outer covering of a bacteria cell is the cell wall which is rigid and provides structural integrity.
The bacteria cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan or murein. Different shapes of bacteria cell are the characteristic feature of a bacteria species. Bacteria cells may contain external appendages like cilia flagella etc.
The surface appearances of bacterial colonies include textures such as smooth rough dull glistening wrinkled mucoid and spreading. Buttery viscid sticky brittle or friable dry mucoid. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus nuclear membrane.
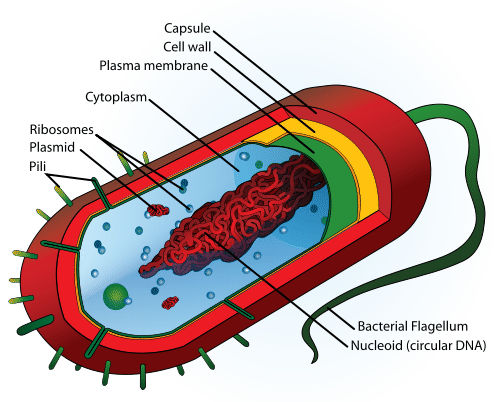
Plants animals fungi and protists a very heterogeneous group that are neither animals plants or fungi and are often single cell and small eg protozoa. Bacterial cells prokaryotic cells are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 32. They consists of various cell surface structures cell wall plasma membrane many cytoplasmic inclusions and the bacterial chromosome nucleoid.
Except some all structures do not occur in every genus. These are unicellular organisms found everywhere on earth from soil to the human body. They have different shapes and structures.
The cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan that provides structure to the cell wall. Bacteria have some unique. CAPSULES are slippery structures found exterior to the cell wall of many bacteria.
Capsules may be involved in bacterial virulence cells with capsules are less likely to be phagocytized or in bacterial adherence such as the adherence of Streptococcus mutans to teeth. Capsules are normally composed of polymers of sugars andor proteins. Bacterial Endospores Structure Characteristics Significance Formation and Germination of Bacterial Endospores What are Endospores.
Bacterial endospores are special tough dormant and resistant spores produced by some Gram-positive bacteria of Firmicute family during unfavorable environmental conditions. Endospores are developed within the vegetative cells hence the name endo inside. Bacteria display an array of contact-dependent interaction systems that have evolved to facilitate direct cell-to-cell communication.
We have previously identified a mode of bacterial communication mediated by nanotubes bridging neighboring cells. Here we elucidate nanotube architecture dynamics and molecular components. Pathogenic bacteria are known for their ability to produce a wide variety of toxins upon invading a host cell and these substances help to increase their pathogenicity and virulence in vivo.
Bacteria that produce toxins are said to be toxigenic in nature. Toxins when produced may be transported by blood and lymph fluids. And they cause cytotoxic effects at tissue sites distant from the.
Morphology of bacterial cell deals with study of. Size of bacterial cell is less than 3 micrometer. The bacteria are microscopic in nature and are visible only under compound microscope.
These bacteria may be sphericalcylindrical or spiral in shape.